TS
MuslimAirForce
Iran Army Meluncurkan Strategic Space & Satellite Detecting Sepehr Radars
Iran Army Meluncurkan Strategic Space & Satellite Detecting Over-the-horizon Sepehr Radars
Iran Plans to Start Using New Types of Radars in Coming Months
TEHRAN (FNA)- Iran plans to boost its air-defense capability with new types of radar systems, including satellite detecting radars, a senior Iranian commander announced on Tuesday.
Speaking to reporters here in Tehran today, Commander of Khatam ol-Anbia Air Defense Base Brigadier General Farzad Esmayeeli said Iran has equipped its air-defense units with Qader, Mersad, Ya Zahra 3, Misaq 2 and strategic independent S-200 air defense missiles in the current Iranian year (March 20, 2012-March 20, 2013).
"As regards our radar systems, we started using Samen, Shahab and Matla radar systems (this year) and we hope to start deploying and using Arash radars as well as strategic space (satellite detecting) Sepehr radars next (Iranian) year (March 21, 2013 - March 20, 2014)," Esmayeeli added.
In February, Iranian Defense Minister Brigadier General Ahmad Vahidi said that Iran plans to develop different types of radar systems with satellite detecting capabilities.
Addressing the second conference on radar technology systems here in Tehran at the time, Vahidi said Iran has witnessed "a jump" in the field of radar designing and manufacturing.
"Today, we have many achievements in different fields. Radars covering ranges of 500km to 700km have been manufactured and production of radar systems with 1,000km to 3,000km of range is underway," Vahidi explained.
He added that Iran is trying to develop radar systems to detect satellites, and said to do so, the radar systems are connected in phased arrangements to cover very long ranges and detect and track satellites.
Iranian officials have announced that the country has now reached self-sufficiency in producing radar systems in different frequencies and for various ranges.
http://english.farsnews.com/newstext...?nn=9107152378
Army Commander: Iran to Unveil New Military Achievements
TEHRAN (FNA)- The Iranian Army's Deputy Top Liaison, General Mohammad Hossein Dadras, stressed that Iran enjoys the ability to supply the country's Armed Forces with their needed military tools and equipment without foreign assistance, and added that the country plans to unveil new air defense systems in the near future.
The official noted that the Islamic Republic has achieved self-sufficiency in various military industries, so that it indigenously produces vessels, aircraft, radars and ammunitions without any need to foreign imports.
Dadras also announced that a major radar system will soon be unveiled.
Despite its vast geographical area, Iran is capable of detecting drones with "small cross-section on radar," Dadras pointed out, stressing that the country has no concern in the field of air defense as its skies are fully controlled by the armed forces.
On Tuesday, a senior Iranian commander announced that Iran plans to boost its air-defense capability with new types of radar systems, including satellite detecting radars.
Speaking to reporters here in Tehran, Commander of Khatam ol-Anbia Air Defense Base Brigadier General Farzad Esmayeeli said Iran has equipped its air-defense units with Qader, Mersad, Ya Zahra 3, Misaq 2 and strategic independent S-200 air defense missiles in the current Iranian year (March 20, 2012-March 20, 2013).
"As regards our radar systems, we started using Samen, Shahab and Matla radar systems (this year) and we hope to start deploying and using Arash radars as well as strategic space (satellite detecting) Sepehr radars next (Iranian) year (March 21, 2013 - March 20, 2014)," Esmayeeli added.
In February, Iranian Defense Minister Brigadier General Ahmad Vahidi said that Iran plans to develop different types of radar systems with satellite detecting capabilities.
Addressing the second conference on radar technology systems here in Tehran at the time, Vahidi said Iran has witnessed "a jump" in the field of radar designing and manufacturing.
"Today, we have many achievements in different fields. Radars covering ranges of 500km to 700km have been manufactured and production of radar systems with 1,000km to 3,000km of range is underway," Vahidi explained.
He added that Iran is trying to develop radar systems to detect satellites, and said to do so, the radar systems are connected in phased arrangements to cover very long ranges and detect and track satellites.
Iranian officials have announced that the country has now reached self-sufficiency in producing radar systems in different frequencies and for various ranges.
Iran has also taken wide strides in designing and manufacturing different types of light, semi-heavy and heavy weapons, military tools and equipment. Tehran launched an arms development program during the 1980-88 Iraqi imposed war on Iran to compensate for a US weapons embargo. Since 1992, Iran has produced its own tanks, armored personnel carriers, missiles and fighter planes.
Yet, Iranian officials have always stressed that the country's military and arms programs serve defensive purposes and should not be perceived as a threat to any other country.
http://english.farsnews.com/newstext...?nn=9107152668

OTH systems
US Navy
Coverage of the three US Navy ROTHR stations in Texas, Virginia, and Puerto Rico
The US Navy also created their own system, the AN/TPS-71 ROTHR (Relocatable Over-the-Horizon Radar), which covers a 64 degree wedge-shaped area at ranges between 500 to 1,600 nautical miles (925 to 3,000 km). ROTHR was originally intended to keep track of ship and aircraft movement over the Pacific, and thus allow coordinated fleet movements well in advance of an engagement. A prototype ROTHR system was installed on the isolated Aleutian Island of Amchitka, Alaska, monitoring the eastern coast of Russia, in 1991 and used until 1993. The equipment was later removed into storage. The first production systems were installed in the test site in Virginia for acceptance testing but were then transitioned to counter the illegal drug trade, covering Central America and the Caribbean. The second production ROTHR was later set up in Texas, covering many of the same areas in the Caribbean, but also providing coverage over the Pacific as far south as Colombia. It also operates in the anti-drug trafficking role. The third, and final, production system was installed in Puerto Rico, extending counterdrug surveillance past the equator, deep into South America.
USSR/Russia
The Soviets had also studied OTH systems starting as early as the 1950s. Their first experimental model appears to be the Veyer (Hand Fan) that was built in 1949. The next serious Soviet project was Duga-2, built outside Nikolayev (on the Black Sea coast near Odessa). Aimed eastward, Duga-2 was first started on 7 November 1971, and was successfully used to track missile launches from the far east and Pacific Ocean to the testing ground on Novaya Zemlya.
This was followed by their first operational system, known in the west as Steel Yard, which first broadcast in 1976. Built outside Gomel, near Chernobyl, it was aimed northward and covered the continental USA. Its loud and repetitive pulses in the middle of the shortwave radio bands led to it being known as the Russian Woodpecker by amateur radio (ham) operators. The Soviets eventually shifted the frequencies they used, without admitting they were even the source, largely due to its interference with certain long-range air-to-ground communications used by commercial airliners. A second system was set up in Siberia, also covering the continental USA, as well as Alaska.
Australia
Official coverage of the Jindalee Operational Radar Network.
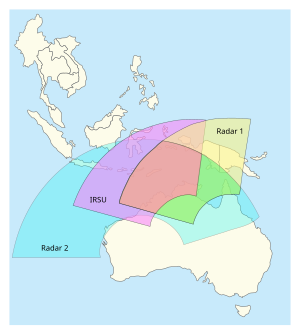
A more recent addition is the Jindalee Operational Radar Network developed by the Australian Department of Defence in 1998 and completed in 2000. It is operated by No. 1 Radar Surveillance Unit of the Royal Australian Air Force. Jindalee is a multistatic radar (multiple-receiver) system using OTH-B, allowing it to have both long range as well as anti-stealth capabilities. It has an official range of 3,000 kilometres (1,900 mi) but in 1997 the prototype was able to detect missile launches by China[5] over 5,500 kilometres (3,400 mi) away.
Jindalee uses 560 kW as compared to the US's OTH-B's 1 MW, yet offers far better range than the US 1980s system, due to the considerably improved electronics and signal processing.[6]
France
The French have developed an OTH radar called NOSTRADAMUS[7] (stands for New Transhorizon Decametric System Applying Studio Methods) during the 1990s. It entered in service for the French army in 2005, but is still in development. It is based on a star shaped antenna field used for emission and reception (monostatic) able to detect every aircraft at more than one thousand kilometers, in a 360 degree arc. The frequency range used is from 6 to 30 MHz.
China
A number of OTH-B and OTH-SW radars are reportedly in operation in China. Few details are known of these systems. However, transmission from these radars cause lot of interference to other international licensed users.[8][9][10]
Iran
Iran is working on an OTH radar called Sepehr with reported range of 3,000 kilometers.[11]It is scheduled to enter operational status in 2013[12]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Over-t...-horizon_radar
Iran Plans to Start Using New Types of Radars in Coming Months
TEHRAN (FNA)- Iran plans to boost its air-defense capability with new types of radar systems, including satellite detecting radars, a senior Iranian commander announced on Tuesday.
Speaking to reporters here in Tehran today, Commander of Khatam ol-Anbia Air Defense Base Brigadier General Farzad Esmayeeli said Iran has equipped its air-defense units with Qader, Mersad, Ya Zahra 3, Misaq 2 and strategic independent S-200 air defense missiles in the current Iranian year (March 20, 2012-March 20, 2013).
"As regards our radar systems, we started using Samen, Shahab and Matla radar systems (this year) and we hope to start deploying and using Arash radars as well as strategic space (satellite detecting) Sepehr radars next (Iranian) year (March 21, 2013 - March 20, 2014)," Esmayeeli added.
In February, Iranian Defense Minister Brigadier General Ahmad Vahidi said that Iran plans to develop different types of radar systems with satellite detecting capabilities.
Addressing the second conference on radar technology systems here in Tehran at the time, Vahidi said Iran has witnessed "a jump" in the field of radar designing and manufacturing.
"Today, we have many achievements in different fields. Radars covering ranges of 500km to 700km have been manufactured and production of radar systems with 1,000km to 3,000km of range is underway," Vahidi explained.
He added that Iran is trying to develop radar systems to detect satellites, and said to do so, the radar systems are connected in phased arrangements to cover very long ranges and detect and track satellites.
Iranian officials have announced that the country has now reached self-sufficiency in producing radar systems in different frequencies and for various ranges.
http://english.farsnews.com/newstext...?nn=9107152378
Army Commander: Iran to Unveil New Military Achievements
TEHRAN (FNA)- The Iranian Army's Deputy Top Liaison, General Mohammad Hossein Dadras, stressed that Iran enjoys the ability to supply the country's Armed Forces with their needed military tools and equipment without foreign assistance, and added that the country plans to unveil new air defense systems in the near future.
The official noted that the Islamic Republic has achieved self-sufficiency in various military industries, so that it indigenously produces vessels, aircraft, radars and ammunitions without any need to foreign imports.
Dadras also announced that a major radar system will soon be unveiled.
Despite its vast geographical area, Iran is capable of detecting drones with "small cross-section on radar," Dadras pointed out, stressing that the country has no concern in the field of air defense as its skies are fully controlled by the armed forces.
On Tuesday, a senior Iranian commander announced that Iran plans to boost its air-defense capability with new types of radar systems, including satellite detecting radars.
Speaking to reporters here in Tehran, Commander of Khatam ol-Anbia Air Defense Base Brigadier General Farzad Esmayeeli said Iran has equipped its air-defense units with Qader, Mersad, Ya Zahra 3, Misaq 2 and strategic independent S-200 air defense missiles in the current Iranian year (March 20, 2012-March 20, 2013).
"As regards our radar systems, we started using Samen, Shahab and Matla radar systems (this year) and we hope to start deploying and using Arash radars as well as strategic space (satellite detecting) Sepehr radars next (Iranian) year (March 21, 2013 - March 20, 2014)," Esmayeeli added.
In February, Iranian Defense Minister Brigadier General Ahmad Vahidi said that Iran plans to develop different types of radar systems with satellite detecting capabilities.
Addressing the second conference on radar technology systems here in Tehran at the time, Vahidi said Iran has witnessed "a jump" in the field of radar designing and manufacturing.
"Today, we have many achievements in different fields. Radars covering ranges of 500km to 700km have been manufactured and production of radar systems with 1,000km to 3,000km of range is underway," Vahidi explained.
He added that Iran is trying to develop radar systems to detect satellites, and said to do so, the radar systems are connected in phased arrangements to cover very long ranges and detect and track satellites.
Iranian officials have announced that the country has now reached self-sufficiency in producing radar systems in different frequencies and for various ranges.
Iran has also taken wide strides in designing and manufacturing different types of light, semi-heavy and heavy weapons, military tools and equipment. Tehran launched an arms development program during the 1980-88 Iraqi imposed war on Iran to compensate for a US weapons embargo. Since 1992, Iran has produced its own tanks, armored personnel carriers, missiles and fighter planes.
Yet, Iranian officials have always stressed that the country's military and arms programs serve defensive purposes and should not be perceived as a threat to any other country.
http://english.farsnews.com/newstext...?nn=9107152668

OTH systems
US Navy
Coverage of the three US Navy ROTHR stations in Texas, Virginia, and Puerto Rico
The US Navy also created their own system, the AN/TPS-71 ROTHR (Relocatable Over-the-Horizon Radar), which covers a 64 degree wedge-shaped area at ranges between 500 to 1,600 nautical miles (925 to 3,000 km). ROTHR was originally intended to keep track of ship and aircraft movement over the Pacific, and thus allow coordinated fleet movements well in advance of an engagement. A prototype ROTHR system was installed on the isolated Aleutian Island of Amchitka, Alaska, monitoring the eastern coast of Russia, in 1991 and used until 1993. The equipment was later removed into storage. The first production systems were installed in the test site in Virginia for acceptance testing but were then transitioned to counter the illegal drug trade, covering Central America and the Caribbean. The second production ROTHR was later set up in Texas, covering many of the same areas in the Caribbean, but also providing coverage over the Pacific as far south as Colombia. It also operates in the anti-drug trafficking role. The third, and final, production system was installed in Puerto Rico, extending counterdrug surveillance past the equator, deep into South America.
USSR/Russia
The Soviets had also studied OTH systems starting as early as the 1950s. Their first experimental model appears to be the Veyer (Hand Fan) that was built in 1949. The next serious Soviet project was Duga-2, built outside Nikolayev (on the Black Sea coast near Odessa). Aimed eastward, Duga-2 was first started on 7 November 1971, and was successfully used to track missile launches from the far east and Pacific Ocean to the testing ground on Novaya Zemlya.
This was followed by their first operational system, known in the west as Steel Yard, which first broadcast in 1976. Built outside Gomel, near Chernobyl, it was aimed northward and covered the continental USA. Its loud and repetitive pulses in the middle of the shortwave radio bands led to it being known as the Russian Woodpecker by amateur radio (ham) operators. The Soviets eventually shifted the frequencies they used, without admitting they were even the source, largely due to its interference with certain long-range air-to-ground communications used by commercial airliners. A second system was set up in Siberia, also covering the continental USA, as well as Alaska.
Australia
Official coverage of the Jindalee Operational Radar Network.

A more recent addition is the Jindalee Operational Radar Network developed by the Australian Department of Defence in 1998 and completed in 2000. It is operated by No. 1 Radar Surveillance Unit of the Royal Australian Air Force. Jindalee is a multistatic radar (multiple-receiver) system using OTH-B, allowing it to have both long range as well as anti-stealth capabilities. It has an official range of 3,000 kilometres (1,900 mi) but in 1997 the prototype was able to detect missile launches by China[5] over 5,500 kilometres (3,400 mi) away.
Jindalee uses 560 kW as compared to the US's OTH-B's 1 MW, yet offers far better range than the US 1980s system, due to the considerably improved electronics and signal processing.[6]
France
The French have developed an OTH radar called NOSTRADAMUS[7] (stands for New Transhorizon Decametric System Applying Studio Methods) during the 1990s. It entered in service for the French army in 2005, but is still in development. It is based on a star shaped antenna field used for emission and reception (monostatic) able to detect every aircraft at more than one thousand kilometers, in a 360 degree arc. The frequency range used is from 6 to 30 MHz.
China
A number of OTH-B and OTH-SW radars are reportedly in operation in China. Few details are known of these systems. However, transmission from these radars cause lot of interference to other international licensed users.[8][9][10]
Iran
Iran is working on an OTH radar called Sepehr with reported range of 3,000 kilometers.[11]It is scheduled to enter operational status in 2013[12]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Over-t...-horizon_radar
0
4.5K
0
Thread Digembok
Mari bergabung, dapatkan informasi dan teman baru!
Militer
20KThread•6.8KAnggota
Thread Digembok